In the late 1983s, The original HVLS Fan prototype came to the market with 3 phase belt drive and pulley system. These types of fans are developed for agricultural applications, so early research focuses on the benefits of HVLS fans on dairy production. There has been considerable change happening in technology, functional, and market demands with time. The market of the HVLS fans has increased. Impelling this HVLS fan into the market in order to save energy and money on the HVAC system. Considering the demand for the various applications there will be design & development that occurs in motor and blades. All these developments expand the applications of HVLS fans from the original dairy industry and large scale commercial application to greater use in smaller businesses. HVLS fan provides the best option for the businessman to solve the air problem in the facility with less energy cost of moving air and creating a comfortable environment. This technology helps to improve ventilation and indoor air quality by providing thermal destratification by running in the reverse direction to equalizing air temperatures from floor to ceiling.
Design changes of fan blades
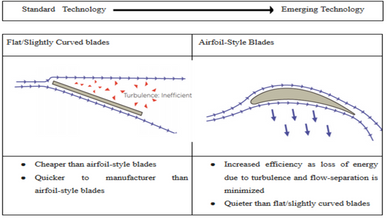
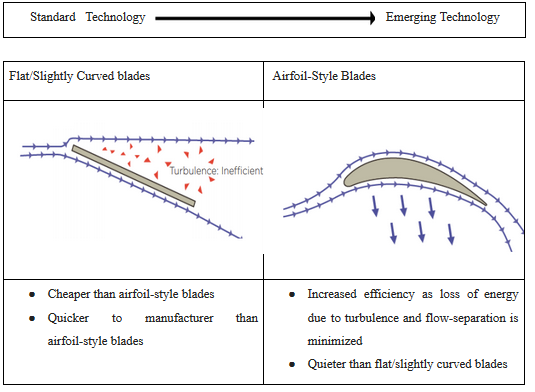
The development in design has improved the performance of HVLS Fan over the year. The design section includes key hardware components. These are blades, motors, controls, and generalized air movement profiles of flat blades and airfoil Blades. The HVLS fan blade design changes from 10 blade to 5 or 3 blades, some manufacturers still offer 10 blade design today. The number of the blade on the fan plays a significant role in its performance. Reduction in the number of the blade can lower the total weight of fans thereby lowering the torque required and the fan can rotate more efficiently. Since torque is the constant stressor of the motor, less torque longer the life. The blade design has improved from flat or slightly curved blade to airfoil blades to increase efficiency.
The optimization of blade design is focused on airspeed, creating uniform airspeed along the fan radius and maximizing airflow coverage. The table below shows the design for the blade, changes over the years.
Table 1: Difference between blade profiles
360 degree of airflow possible with airfoil blade design
HVLS fan blades are designed on the principle of physics and aerodinámica. HVLS fan creates a massive air column towards the floor and when this hits to the floor it changes direction and becomes horizontal floor jet moving in all directions until it reaches the wall, the air moves up towards the ceiling and again come to the fan area in a horizontal way, then again it is thrown down to the floor. Airfoil blade design of the fan keeps the airflow in the same direction rather than diverting it in different ones. This allows the fan to use less energy.
Recent Trends in Motors
The most common types of electric motors used today for fans are the brushed DC motor, the induction motor, the brushless DC motor, and the latest permanent magnet synchronous motor. Important parameters considered in the development of these motors are the size of the motor, the weight, durability, noise, vibration, power, costs, and controllability, all resulting in a search for high operating efficiency at required power levels for a reasonable price. The permanent synchronous motors are a very popular solution in electrical drives because of its advantages. The table below shows the technologies for motors, changing over the years.
Table 2: HVLS Fan Technology in today’s market
Higher Efficiency Epoch PMSM
Motor efficiency increases from Alternating Current (AC) Induction motors to Permanent Magnet Brushless Direct Current (DC) motors. Generally speaking, brushed DC motors have the lowest efficiency. This is mostly due to the use and wear of brushes and commutators. Induction motors are more efficient than the brushed DC motors but have to cope with bearing and windage losses. The permanent magnet synchronous motors have the advantage over the induction motor that PMSM motors have less electrical losses than induction motors. Because they do not have the secondary windings in their rotors, and the magnetic losses of the rotor are also much lower. These motors reach the highest levels of efficiency. The use of high energy permanent magnets also reduces the physical size of the electric motors for the same output levels. This high torque to inertia ratio allows the PMSM motor to provide a much better acceleration rate than the other motor types.
The utilization rate of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) is increasing in the industry today. In the low power range and in applications requiring variable speed control, adopting PMSM can lead to efficiency improvements of up to 10% to 15% when compared with AC induction motors. And allow the possibility of 90% operational efficiency. This type of motor is replacing traditional Induction motor.
For more information about PMSM Technology, you can visit our website
References